Neck pain is a common clinical symptom. Epidemiological investigation shows that neck pain ranks fourth among the reasons that affect daily labor ability. At any time, 15% of people are experiencing neck pain, and this proportion is 20~30% among college students and young people in the workplace. Since neck pain is so common, can it be ignored? Of course not!
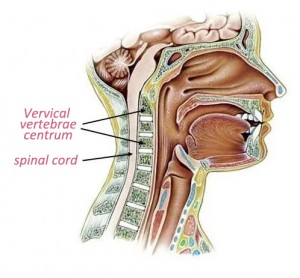
First, let’s take a look at the anatomy of the cervical spine (see the picture below). The cervical vertebra is the upper part of the human spine, which consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, and are connected by ligaments, joints and intervertebral discs. Inside the cervical vertebra, a longitudinal duct is formed from top to bottom, inside which is the spinal cord, which gives off the sensation and movement of nerve roots dominating the limbs. In other words, most of the movements and sensations below the neck (including movements of limbs, internal organs, contraction and relaxation of blood vessels, urination and defecation, and pain) have to pass through this spinal cord in the cervical spinal canal to complete signal transmission. Therefore, it is conceivable that if there is a problem in the cervical spine, there may be too many symptoms, and neck pain is one of the primary signals of cervical spine problems. Should we pay attention to neck pain?
Secondly, there are important blood vessels in the neck, such as cervical spondylolisthesis, abnormal curvature, hyperosteogeny, etc., which can affect blood vessel tension and blood flow velocity through mechanical or reflective factors, thus causing abnormal blood supply to the brain. For brain tissues which are very sensitive to blood supply, long-term insufficient blood supply can cause damage to brain cells, and the consequences can be imagined. Neck pain is an early symptom of abnormal cervical spine alignment and bone lesions. From this perspective, neck pain should be taken seriously.
In addition, the neck muscles provide power for the cervical spine to complete its daily activities. With the popularity of mobile phones, computers and other devices, neck muscles are the most prone to strain in modern society. After cervical muscle strain, not only pain and limited movement, but also secondary hyperosteogeny and cervical instability will occur. Once cervical spine instability occurs, it is often difficult to recover, causing nerve root compression, spinal cord compression and blood vessel compression. Therefore, attention should also be paid to neck pain caused by neck muscle strain.
To sum up, neck pain is the early symptom or the initial symptom of cervical structural and functional problems. Early detection of inducement and active prevention and treatment can avoid serious cervical problems.
Traction is a technique for realigning a broken bone or dislocated part of the body using weights, pulleys, and ropes to gently apply pressure and pull the bone or injured body part back into position. After a fracture, traction can restore the position of a bone during the early stage of healing or temporarily ease the pain while you are waiting for further corrective surgery. There are two main types of traction: skeletal traction and skin traction. A third kind, cervical traction, is used to help stabilize fractures in the neck.
The purpose of traction is to stabilize a fracture or injury and restore tension to the surrounding tissues, muscles, and tendons. Traction can:
1. Stabilize and realign a broken bone or dislocated part of the body (such as the shoulder)
2. Help regain the normal position of the bone that’s been fractured
3. Stretch the neck to reduce pressure on the spine by realigning the vertebrae
4. Temporarily reduce pain prior to surgery
5. Lessen or eliminate muscle spasms and constricted joint, muscles, and tendons
6. Relieve pressure on nerves, especially spinal nerves
7. Treat bone deformities
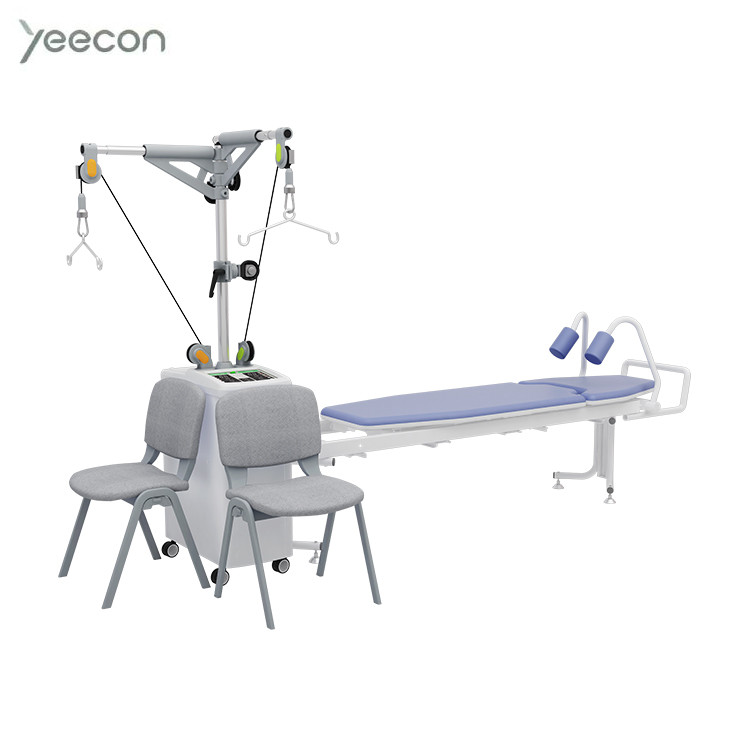

Yeecon Intelligent Traction Table with Heating System YK-6000D
Functions & Features:
1. Two-channel independent operation, double-neck traction configuration, flexible allocation of treatment resources;
2. Heating function: It can heat the neck and waist during traction, automatically recognize the neck and waist heating, and the temperature can be accurately adjusted to improve the treatment effect;
3. Continuous traction, intermittent traction, main and auxiliary traction;
4. Traction force of 0~99KG can be set arbitrarily. And in the traction process, the traction force can be increased or decreased freely, without stopping and setting;
5. Automatic compensation: When the real-time value of the traction force deviates from the set value due to the sudden and unexpected action of the patient, the microcomputer controls the traction host to automatically compensate immediately to ensure the constant traction force and the safety of the patient;
6. Safety design: equipped with two-channel independent emergency stop switch;
7. Set value locking function: it can lock the set traction force and traction time, and will not change the set value due to misoperation;
8. Automatic fault detection, with different codes to indicate the fault. The treatment will stop and resume after trouble shooting.
Indications
1. Cervical vertebra:
Cervical spondylosis, dislocation, cervical muscle spasm, intervertebral disorder, cervical artery distortion, cervical ligament lesion, cervical disc herniation or prolapse, etc.
2. Lumbar spine:
Lumbar spasm, lumbar disc herniation, lumbar functional scoliosis, lumbar degenerative (hypertrophic) osteoarthritis, lumbar synovial tissue incarceration and facet joint disorder caused by acute and chronic lumbar injuries, etc.
Read more:
What is Interferential Current Therapy?
What Can Alternating Magnetic Field Therapy Table Do?
Post time: Apr-24-2022