Stroke has been the leading cause of death in China for the past 30 years, with an incidence rate as high as 39.9% and a mortality rate of over 20%, causing more than 1.9 million deaths every year. Chinese clinicians and rehabilitation associations have compiled a body of knowledge about stroke. Let’s take a closer look.
1. What is Acute Stroke?
A stroke primarily manifests as slurred speech, numbness of limbs, disturbed consciousness, fainting, hemiplegia, and more. It is divided into two categories: 1) Ischemic stroke, which is treated with intravenous thrombolysis and emergency thrombectomy; 2) Hemorrhagic stroke, where the focus is on preventing rebleeding, reducing brain cell damage, and preventing complications.
2. How to Treat It?
1) Ischemic Stroke (Cerebral Infarction)
The optimal treatment for cerebral infarction is ultra-early intravenous thrombolysis, and arterial thrombolysis or thrombectomy can be used for some patients. Thrombolytic therapy with alteplase can be administered within 3-4.5 hours of the onset, and thrombolytic therapy with urokinase can be given within 6 hours of the onset. If the conditions for thrombolysis are met, the thrombolytic therapy with alteplase can effectively reduce the patient’s disability and improve the prognosis. It is important to remember that neurons in the brain cannot regenerate, so the treatment of cerebral infarction must be timely and should not be delayed.

① What is Intravenous Thrombolysis?
Intravenous thrombolytic therapy dissolves the thrombus blocking the blood vessel, recanalizes the obstructed blood vessel, restores the blood supply to the brain tissue promptly, and reduces the necrosis of the brain tissue caused by ischemia. The best time for thrombolysis is within 3 hours after onset.
② What is Emergency Thrombectomy?
Thrombectomy involves a doctor using a DSA machine to remove the emboli blocked in the blood vessel by using a thrombectomy stent or a special suction catheter to achieve cerebral blood vessel recanalization. It is primarily suitable for acute cerebral infarction caused by large vessel occlusion, and the vascular recanalization rate can reach 80%. It is currently the most effective minimally invasive surgery for large vessel occlusive cerebral infarction.
2) Hemorrhagic Stroke
This includes cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, etc. The treatment principle is to prevent rebleeding, reduce brain cell damage caused by cerebral hemorrhage, and prevent complications.
3. How to Identify a Stroke?
1) The patient suddenly experiences balance disorder, walks unsteadily, staggering as if drunk; or the limb strength is normal but lacks accuracy.
2) The patient has blurred vision, double vision, visual field defect; or abnormal eye position.
3) The patient’s mouth corners are crooked and nasolabial folds are shallow.
4) The patient experiences limb weakness, instability in walking or holding objects; or numbness of the limbs.
5) The patient’s speech is slurred and vague.
In case of any abnormalities, it is crucial to act quickly, race against time, and seek medical treatment as soon as possible.

4. How to Prevent Stroke?
1) Hypertensive patients should pay attention to blood pressure control and adhere to medication.
2) Patients with high cholesterol should control their diet and take lipid-lowering drugs.
3) Diabetic patients and high-risk groups should actively prevent and treat diabetes.
4) Those with atrial fibrillation or other heart diseases should actively seek medical attention.
In short, it’s important to eat healthily, exercise moderately, and maintain a positive mood in daily life.
5. The Critical Period of Stroke Rehabilitation
After the acute stroke patient’s condition has stabilized, they should begin rehabilitation and intervention as soon as possible.
Patients with mild to moderate stroke, whose disease will no longer progress, can begin bedside rehabilitation and early bedside rehabilitation training 24 hours after vital signs are stable. Rehabilitation treatment should be started early, and the golden period of rehabilitation treatment is 3 months after a stroke.
Timely and standardized rehabilitation training and treatment can effectively reduce the mortality and disability rates. Therefore, the treatment of stroke patients should include early rehabilitation therapy, in addition to conventional drug treatment. As long as the conditions for early stroke rehabilitation are fully understood and risk factors are closely monitored, the prognosis of patients can be improved, the quality oflife enhanced, hospitalization time shortened, and the cost for patients reduced.
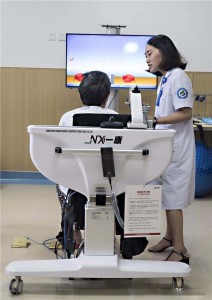
6. Early Rehabilitation
1) Position good limbs on the bed: supine position, lying position on the affected side, group position on the healthy side.
2) Regularly turn over in bed: Regardless of your position, you need to turn over every 2 hours, massage the pressurized parts, and promote blood circulation.
3) Passive activities of hemiplegic limbs: Prevent joint spasms and muscle disuse atrophy when the vital signs are stable 48 hours after the stroke and the primary nervous system disease is stable and no longer progressing.
4) Bed mobility activities: Upper limb and shoulder joint movement, assisted-active turning training, bed bridge exercise training.
Learn to identify the early symptoms of stroke. When a stroke occurs, call the emergency number as soon as possible to buy the patient time for treatment.
Hoping this article is helpful to you.
The article comes from the Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
Post time: Jul-24-2023